Anoxic Brain Damage After Cardiac Arrest - Brain injury is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity among cardiac arrest survivors. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Following anoxic brain injury, a. Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest. Acute hypoperfusion of the brain (e.g., profound shock with impending cardiac arrest). Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Management of these patients in the acute.
It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Acute hypoperfusion of the brain (e.g., profound shock with impending cardiac arrest). Management of these patients in the acute. Brain injury is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity among cardiac arrest survivors. Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Following anoxic brain injury, a.
Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Management of these patients in the acute. Following anoxic brain injury, a. Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest. Brain injury is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity among cardiac arrest survivors. Acute hypoperfusion of the brain (e.g., profound shock with impending cardiac arrest).
Frontiers Long Term Cognitive Function After Cardiac Arrest A Mini
Following anoxic brain injury, a. Acute hypoperfusion of the brain (e.g., profound shock with impending cardiac arrest). Management of these patients in the acute. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest.
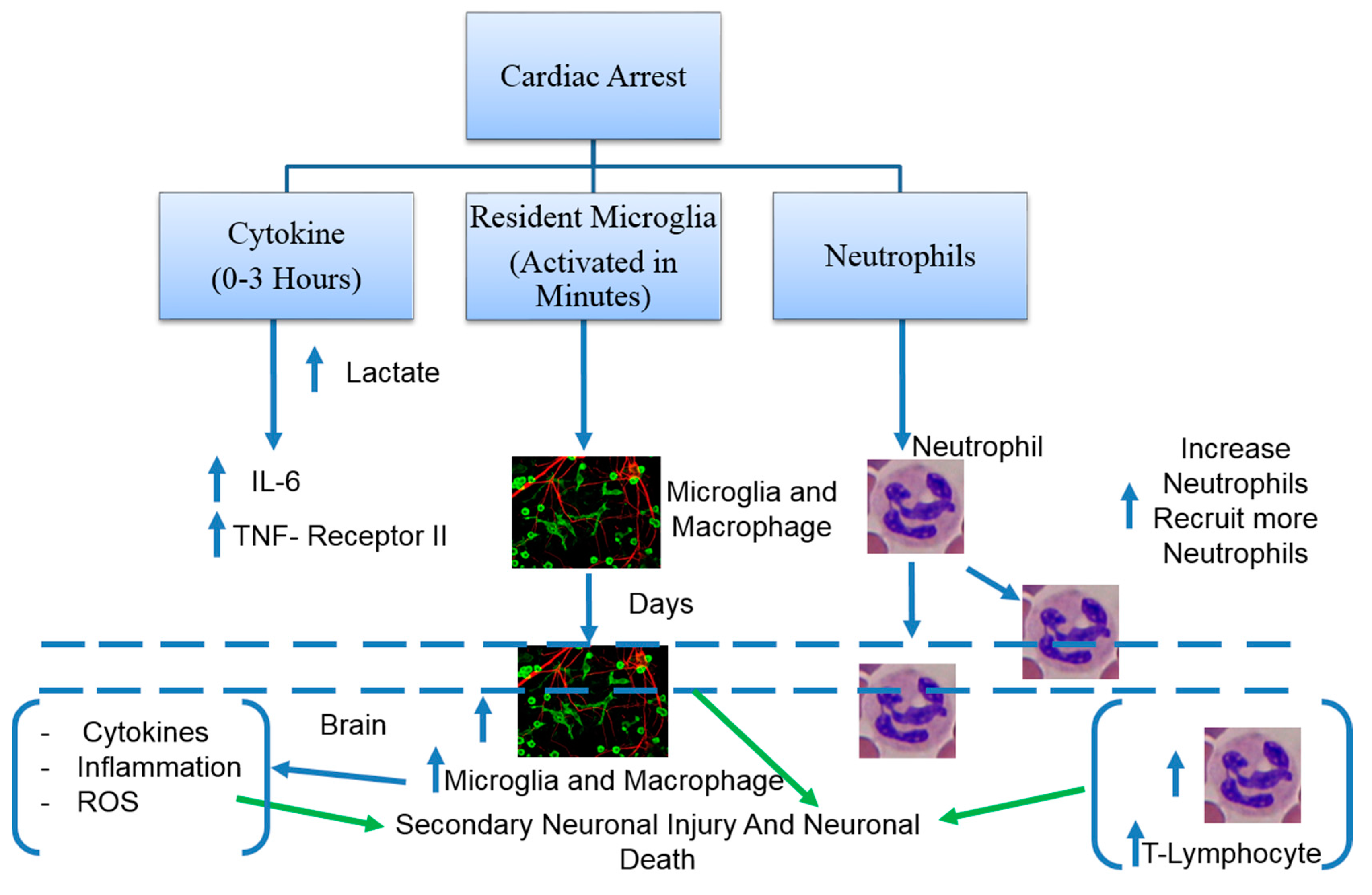
Pathophysiology and the Monitoring Methods for Cardiac Arrest
Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Acute hypoperfusion of the brain (e.g., profound shock with impending cardiac arrest). Brain injury is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity among cardiac arrest survivors. Management of these patients in the acute.
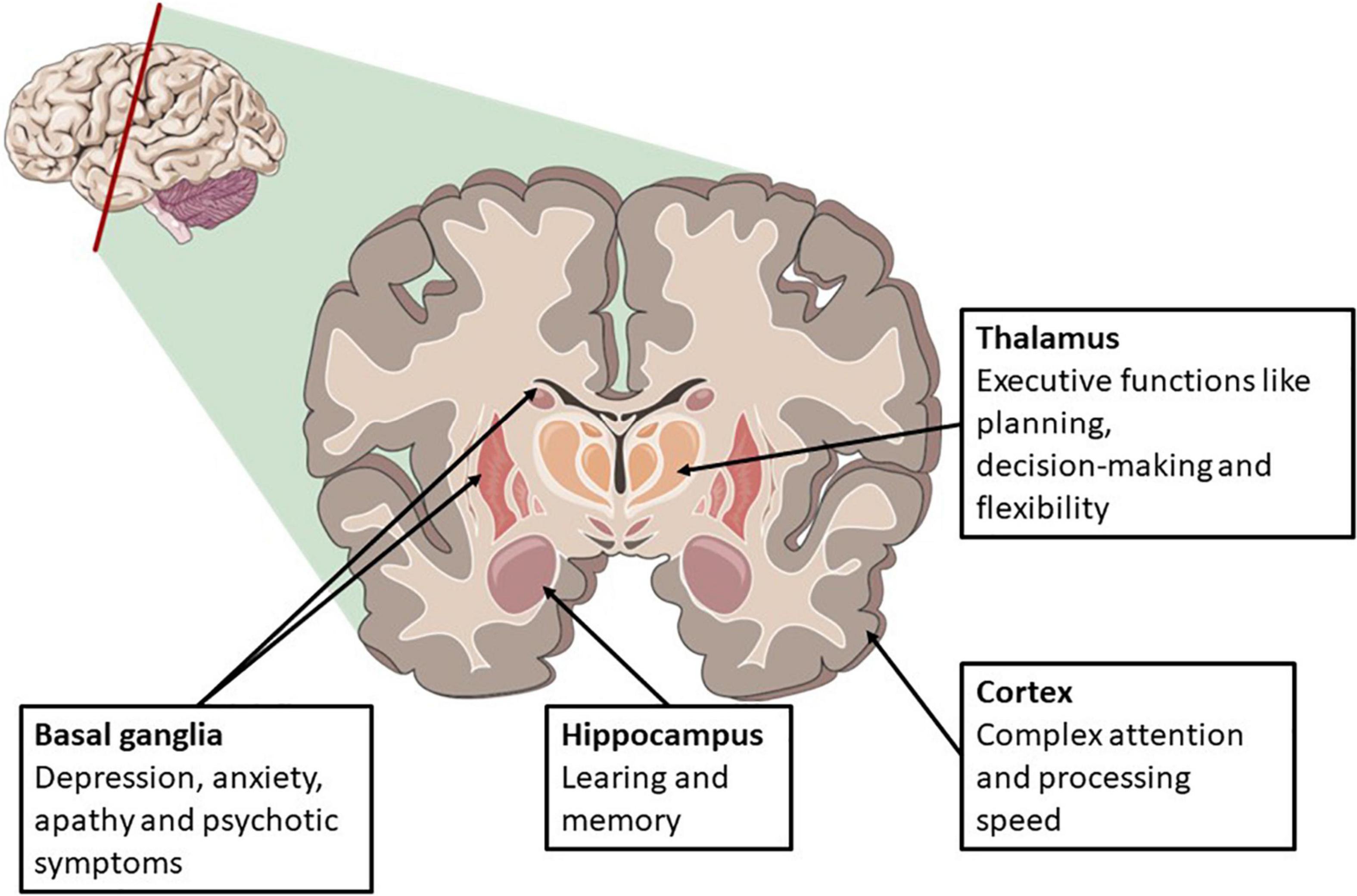
Regional distribution of anoxic brain injury after cardiac arrest
Following anoxic brain injury, a. Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest. Brain injury is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity among cardiac arrest survivors. Acute hypoperfusion of the brain (e.g., profound shock with impending cardiac arrest). Management of these patients in the acute.
Regional distribution of anoxic brain injury after cardiac arrest
Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Management of these patients in the acute. Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest. Following anoxic brain injury, a. It is most likely that ongoing advances in.
Facial Myoclonus Status From Anoxic‐Ischemic Brain Injury Due to
Following anoxic brain injury, a. Acute hypoperfusion of the brain (e.g., profound shock with impending cardiac arrest). Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest.
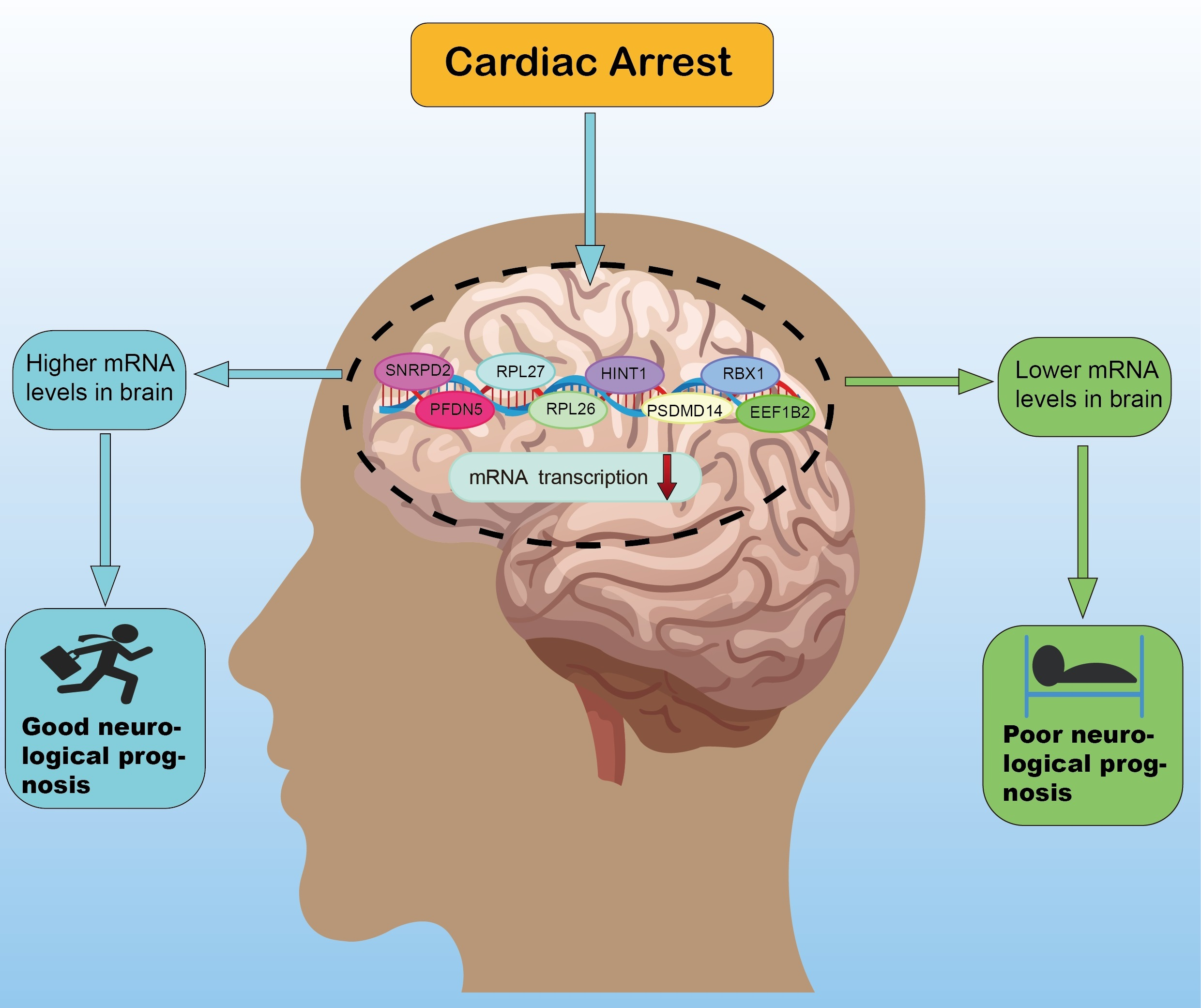
Identification and Validation of Novel Potential Pathogenesis and
Following anoxic brain injury, a. Brain injury is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity among cardiac arrest survivors. Management of these patients in the acute. Acute hypoperfusion of the brain (e.g., profound shock with impending cardiac arrest). Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
Following anoxic brain injury, a. Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest. Management of these patients in the acute. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Acute hypoperfusion of the brain (e.g., profound shock with impending cardiac arrest).
Brain injury after cardiac arrest The Lancet
Brain injury is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity among cardiac arrest survivors. Management of these patients in the acute. Acute hypoperfusion of the brain (e.g., profound shock with impending cardiac arrest). Following anoxic brain injury, a. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field.
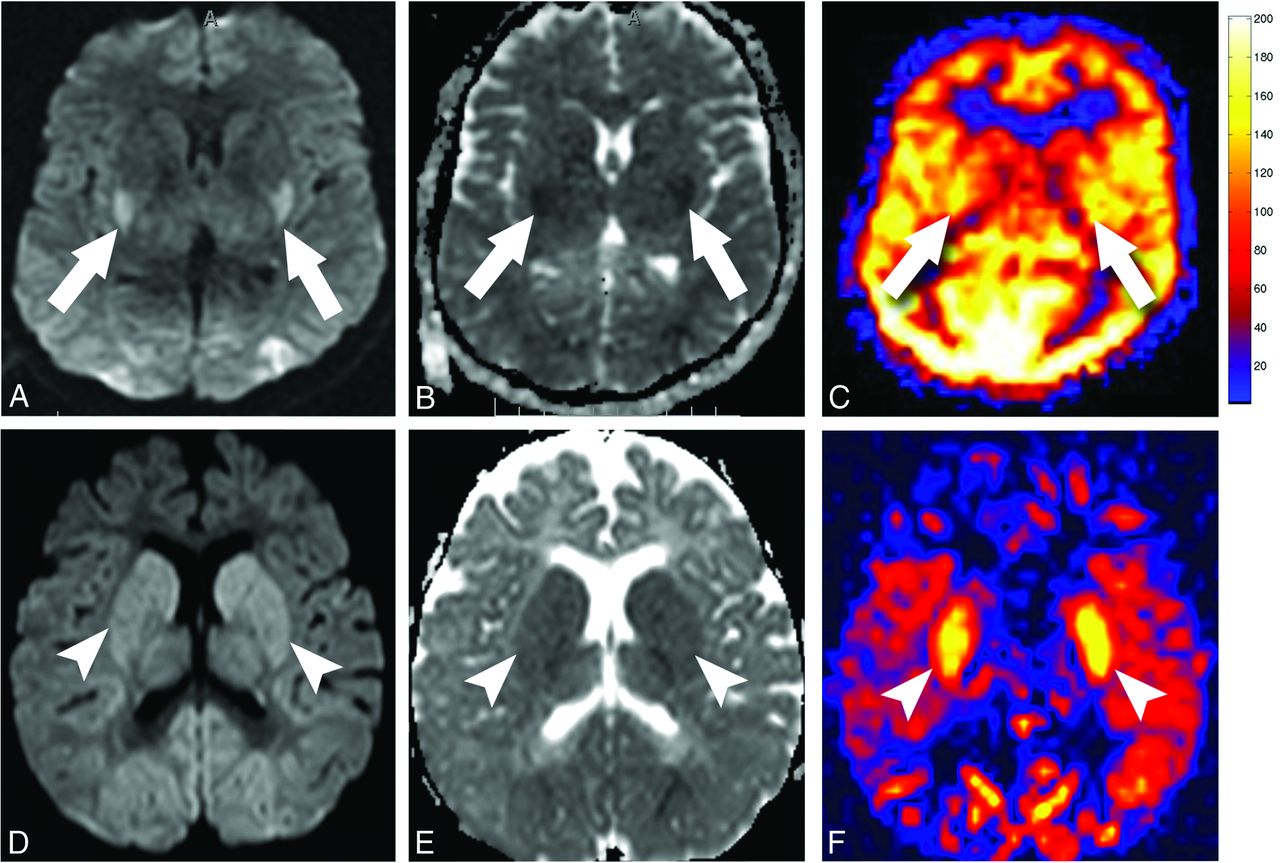
Anoxic Brain Injury Detection with the Normalized Diffusion to ASL
Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest. Following anoxic brain injury, a. Management of these patients in the acute. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field.
Regional distribution of anoxic brain injury after cardiac arrest
Management of these patients in the acute. Brain injury is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity among cardiac arrest survivors. It is most likely that ongoing advances in. Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest. Acute hypoperfusion of the brain (e.g., profound shock with impending cardiac arrest).
Following Anoxic Brain Injury, A.
Brain injury after cardiac arrest constitutes a rapidly developing research field. Management of these patients in the acute. Brain injury is a leading cause of mortality and morbidity among cardiac arrest survivors. It is most likely that ongoing advances in.
Acute Hypoperfusion Of The Brain (E.g., Profound Shock With Impending Cardiac Arrest).
Monitoring and modifying brain oxygenation in patients at risk of hypoxic ischaemic brain injury after cardiac arrest.