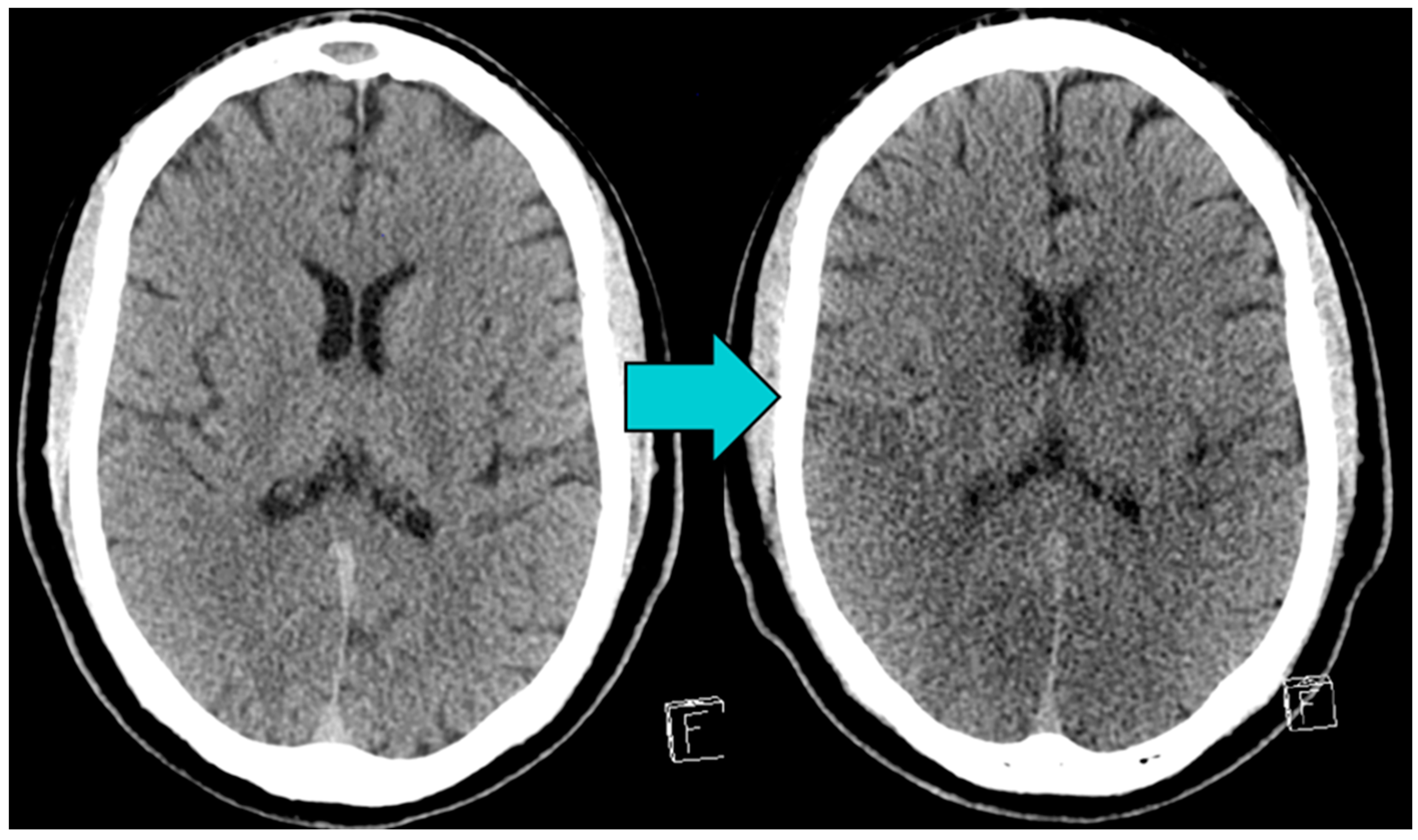
Brain Swelling After Cardiac Arrest - Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still go on to die from the sequelae of anoxic brain. We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in neurologic outcome following cardiac arrest, to understand whether cerebral edema. In this issue of neurocritical care, nakayama et al. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,.
In this issue of neurocritical care, nakayama et al. We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in neurologic outcome following cardiac arrest, to understand whether cerebral edema. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still go on to die from the sequelae of anoxic brain.
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still go on to die from the sequelae of anoxic brain. We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in neurologic outcome following cardiac arrest, to understand whether cerebral edema. In this issue of neurocritical care, nakayama et al.
Patient . After cardiac arrest, a request is submitted to rule out
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in neurologic outcome following cardiac arrest, to understand whether cerebral edema. Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still.
Automated assessment of early hypoxic brain edema in nonenhanced CT
We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in neurologic outcome following cardiac arrest, to understand whether cerebral edema. Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still go on to die from the sequelae of anoxic brain. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and.
The critically ill brain after cardiac arrest Medicherla 2022
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still go on to die from the sequelae of anoxic brain. We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in.
Brain imaging in comatose survivors of cardiac arrest
We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in neurologic outcome following cardiac arrest, to understand whether cerebral edema. Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still go on to die from the sequelae of anoxic brain. In this issue of neurocritical care, nakayama et al. In addition to cell death,.
Managing Cardiac Arrest Therapeutic Hypothermia by
In this issue of neurocritical care, nakayama et al. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in neurologic outcome following cardiac arrest, to understand whether cerebral edema. Most patients who are treated in.
Regional distribution of anoxic brain injury after cardiac arrest
In this issue of neurocritical care, nakayama et al. Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still go on to die from the sequelae of anoxic brain. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. We sought.
Brain MRI of the patient (L. B.) 2 weeks after cardiac arrest. Note
Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still go on to die from the sequelae of anoxic brain. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in neurologic outcome following cardiac arrest, to understand whether cerebral edema. In this issue of neurocritical care, nakayama et al. Most patients who are treated in.
Radiomics for Predicting the Development of Brain Edema from Normal
We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in neurologic outcome following cardiac arrest, to understand whether cerebral edema. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still.
Neuroprognostication After Cardiac Arrest CHEST Critical Care
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in neurologic outcome following cardiac arrest, to understand whether cerebral edema. Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still.
In Addition To Cell Death, Chemical Changes In The Brain During Cardiac Arrest And Reperfusion Can Trigger Cerebral Edema, Or Swelling In The Brain,.
In this issue of neurocritical care, nakayama et al. Most patients who are treated in the hospital after achieving return of spontaneous circulation still go on to die from the sequelae of anoxic brain. We sought to review the role that cerebral edema plays in neurologic outcome following cardiac arrest, to understand whether cerebral edema.