Cardiac Arrest Brain Damage - In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
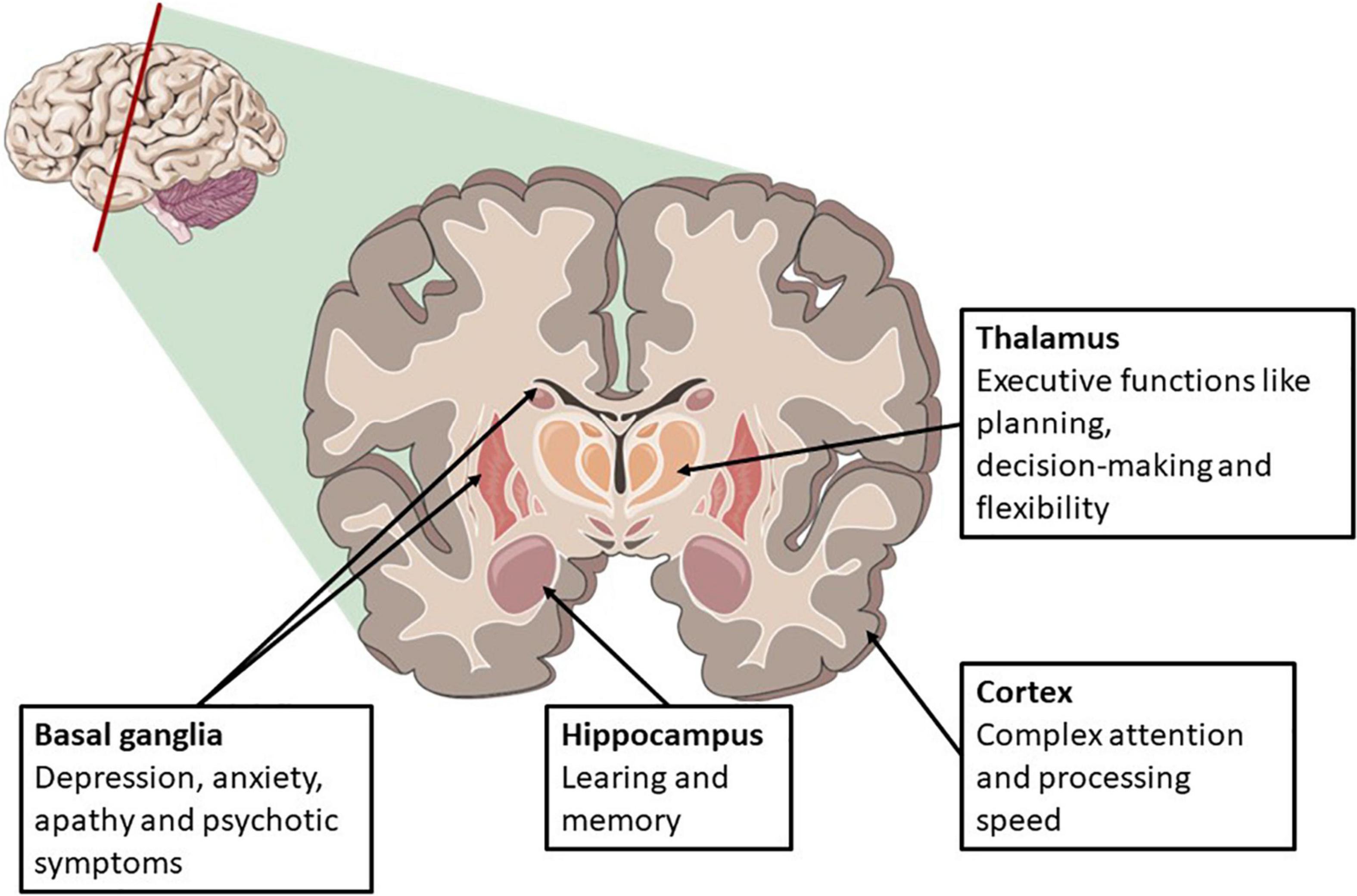
Regional distribution of anoxic brain injury after cardiac arrest
Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,.
Brain Hypoxia Is Associated With Neuroglial Injury in Humans Post
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation for Out‐of‐Hospital
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
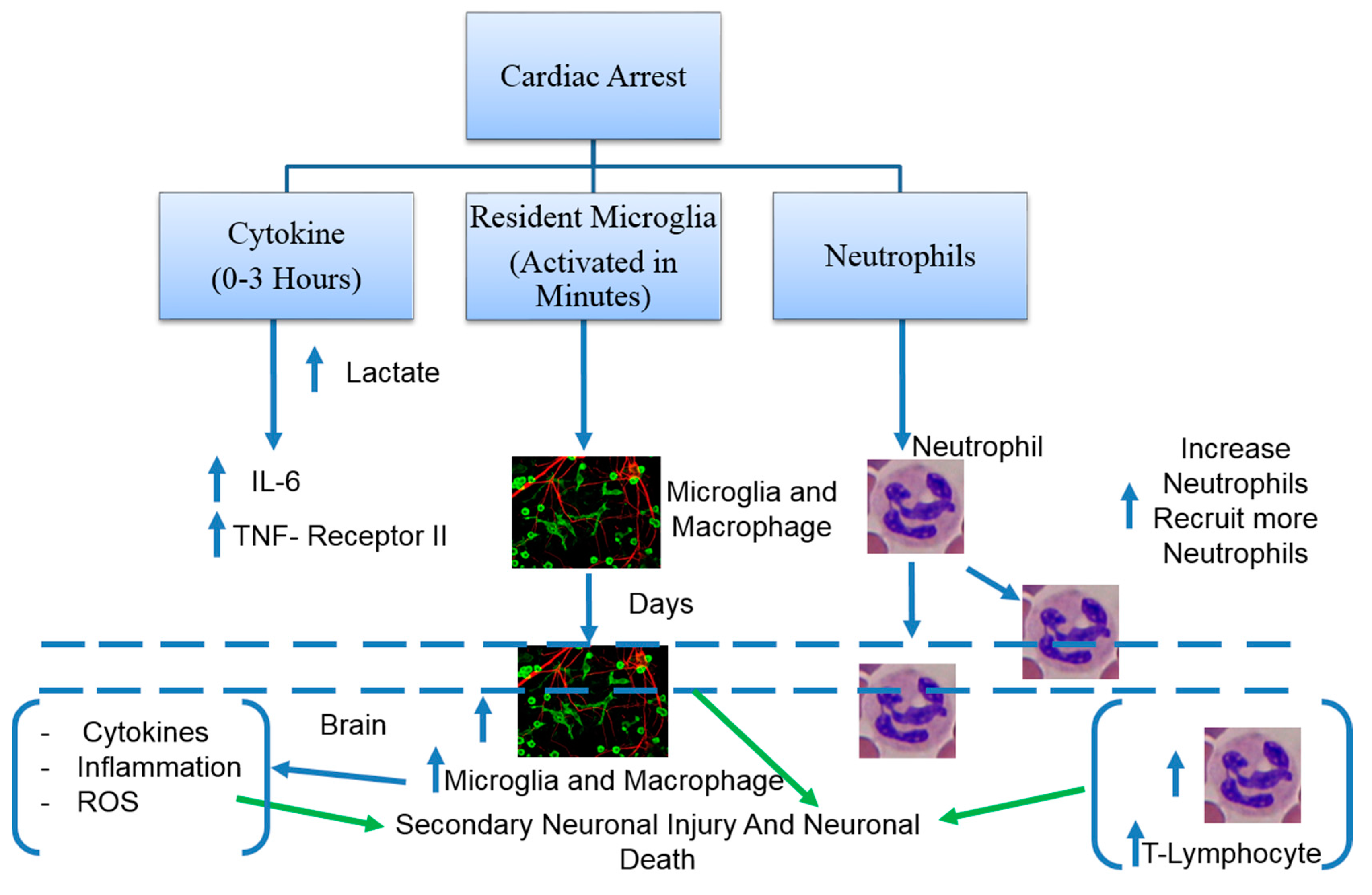
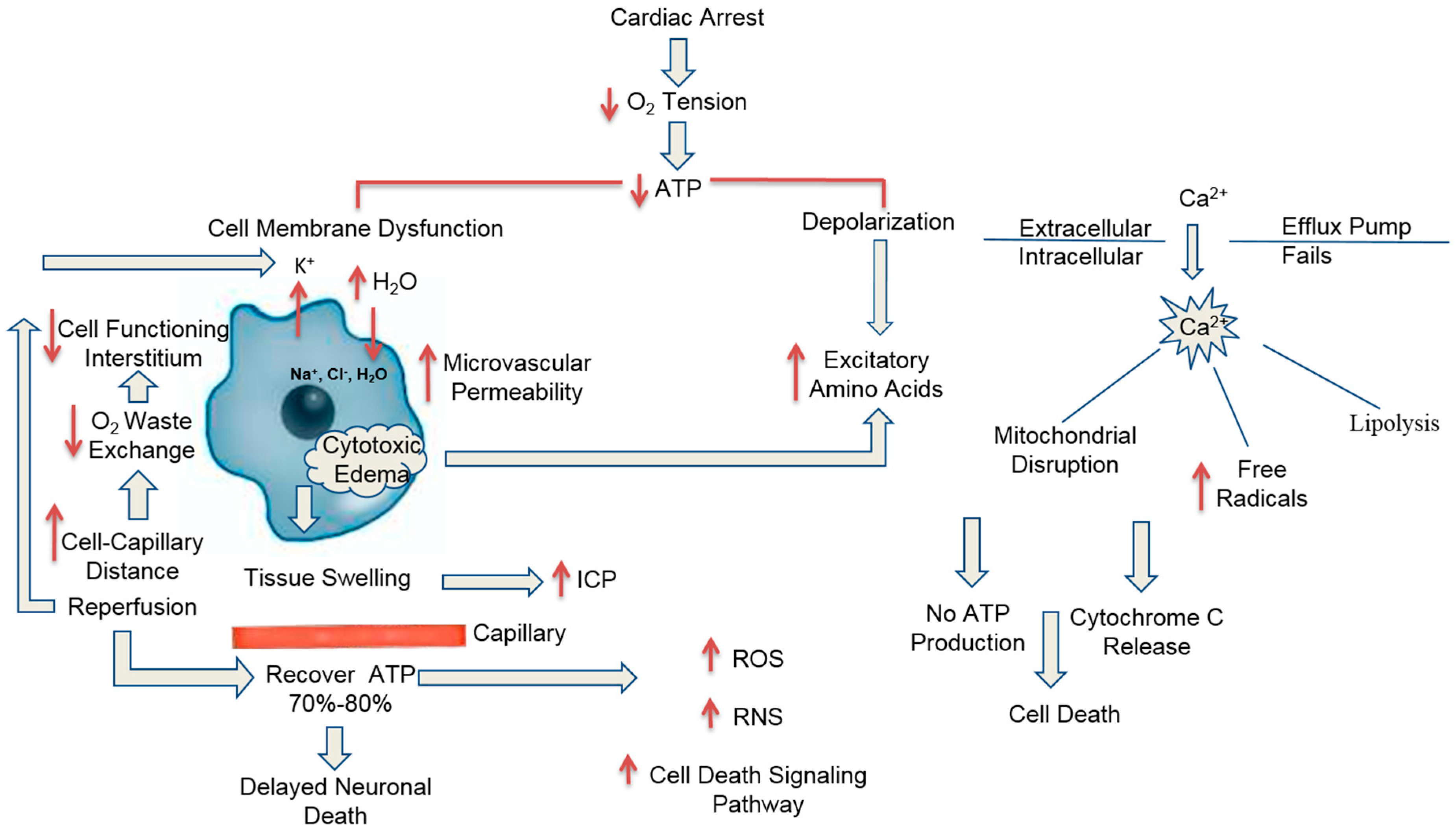
Pathophysiology and the Monitoring Methods for Cardiac Arrest
Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,.
Frontiers Long Term Cognitive Function After Cardiac Arrest A Mini
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
Brain injury after cardiac arrest The Lancet
Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating. In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,.
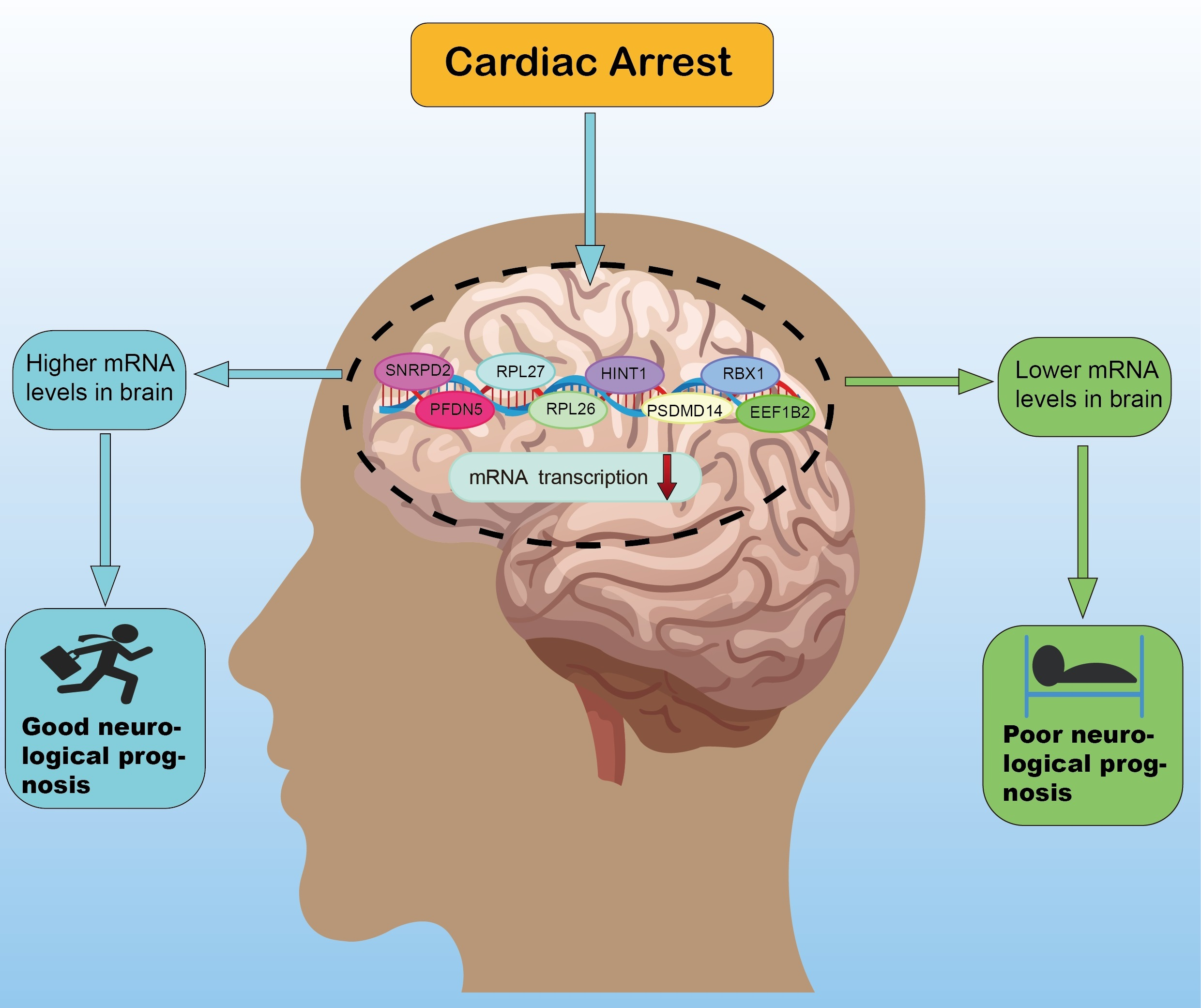
Identification and Validation of Novel Potential Pathogenesis and
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
Pathophysiology and the Monitoring Methods for Cardiac Arrest
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
Improving After PostCardiac Arrest Brain Injury A Scientific
In addition to cell death, chemical changes in the brain during cardiac arrest and reperfusion can trigger cerebral edema, or swelling in the brain,. Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.
In Addition To Cell Death, Chemical Changes In The Brain During Cardiac Arrest And Reperfusion Can Trigger Cerebral Edema, Or Swelling In The Brain,.
Brain injury after resuscitation, a common sequela following cardiac arrest, ranges in severity from mild impairment to devastating.