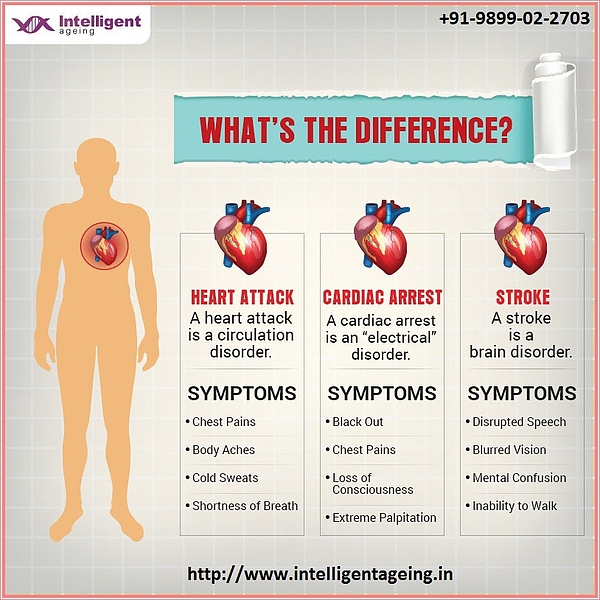
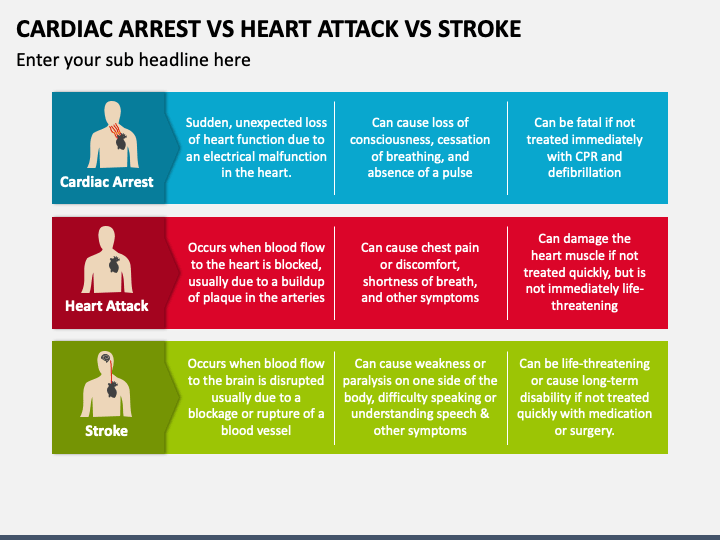
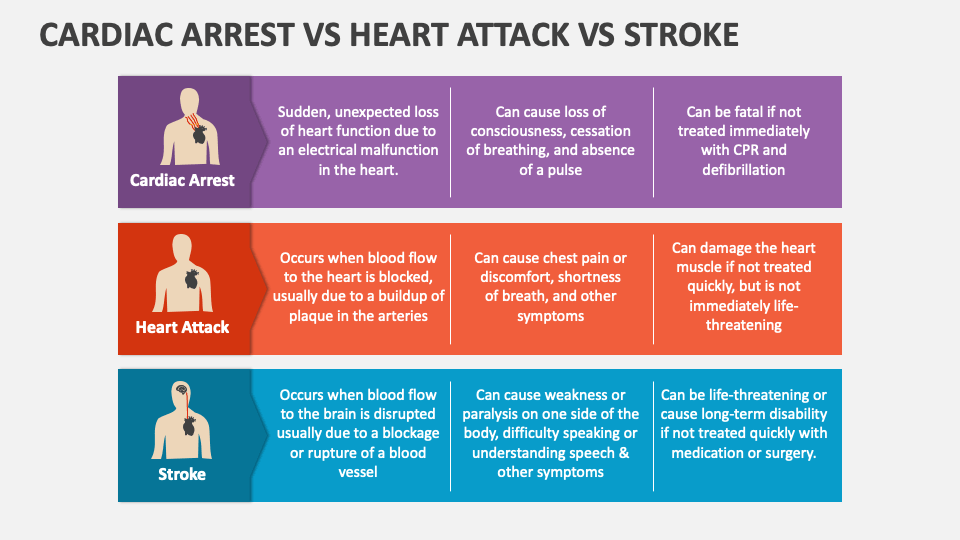
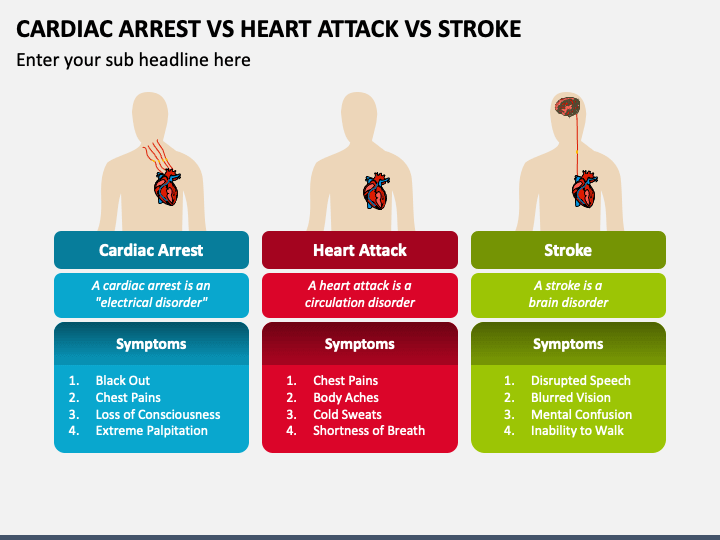
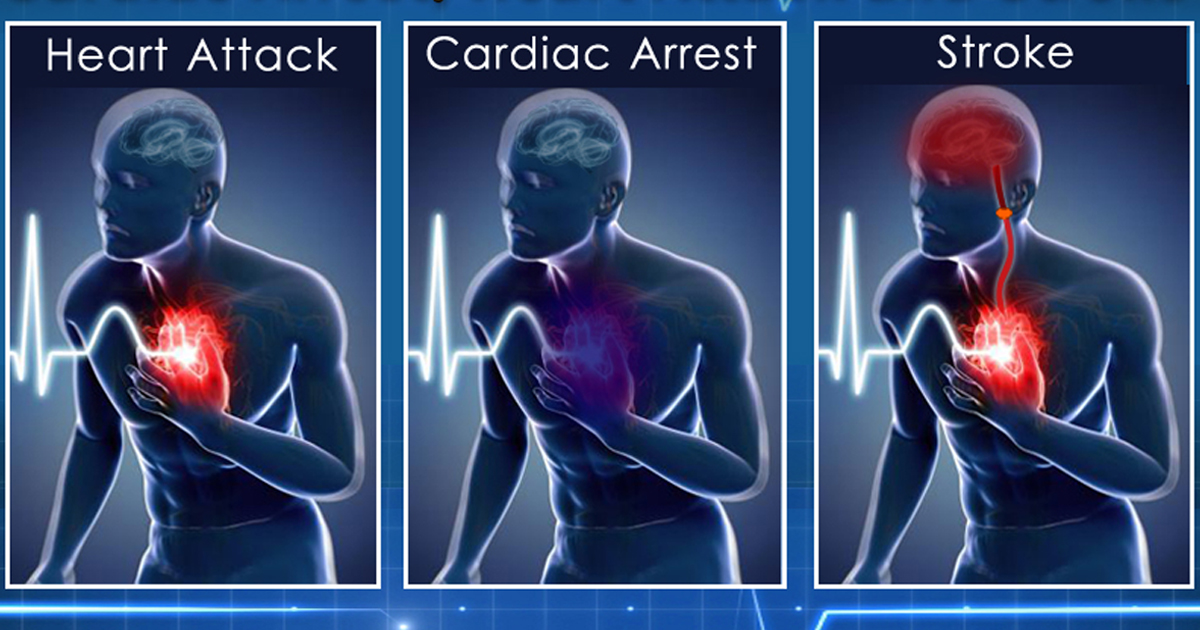
Cardiac Arrest Vs Stroke - Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up.
Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up.
Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up.
What is The Difference Between Stroke, Heart Attack and Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up. Yet, they are different emergencies.
Cardiac Arrest Vs Heart Attack Vs Stroke PowerPoint and Google Slides
Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up. Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain.
Cardiac Arrest vs. Heart Attack vs. Stroke Key Differences Healthy
Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up.
Cardiac Arrest Vs Heart Attack Vs Stroke PowerPoint and Google Slides
Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up.
Cardiac Arrest Vs Heart Attack Vs Stroke PowerPoint and Google Slides
Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up.
Understanding Cardiac Arrest, Heart Attack, and Stroke
Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up.
Learn the Key Differences Among, Cardiac Arrest, Heart Attack and
Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Yet, they are different emergencies.
Understanding Heart Attack, Cardiac Arrest and Stroke Top 10 Home
Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up.
Cardiac Arrest vs. Heart Attack What's The Difference? Coronary
Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain. Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up.
Know the difference between a heart attack, a cardiac arrest and a
Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest, heart attack, and stroke are often mixed up. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain.
Cardiac Arrest, Heart Attack, And Stroke Are Often Mixed Up.
Yet, they are different emergencies. Cardiac arrest is brought on by irregular beating of the heart that causes it to stop supplying blood flow to the other organs, including the brain.