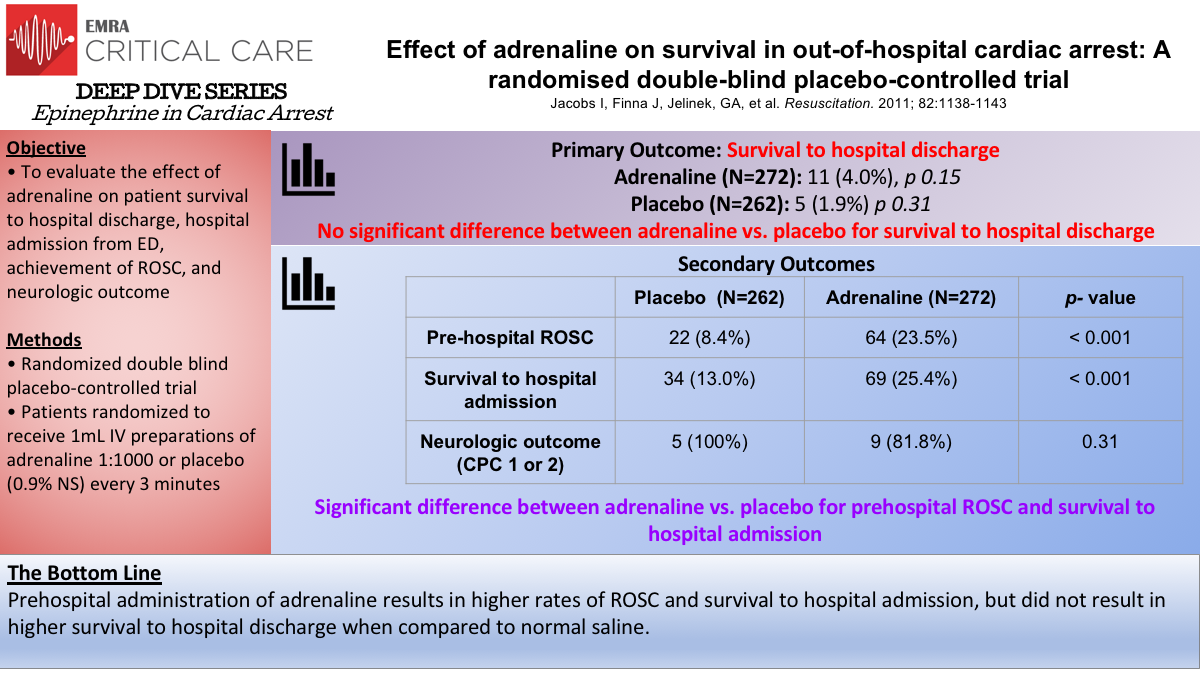
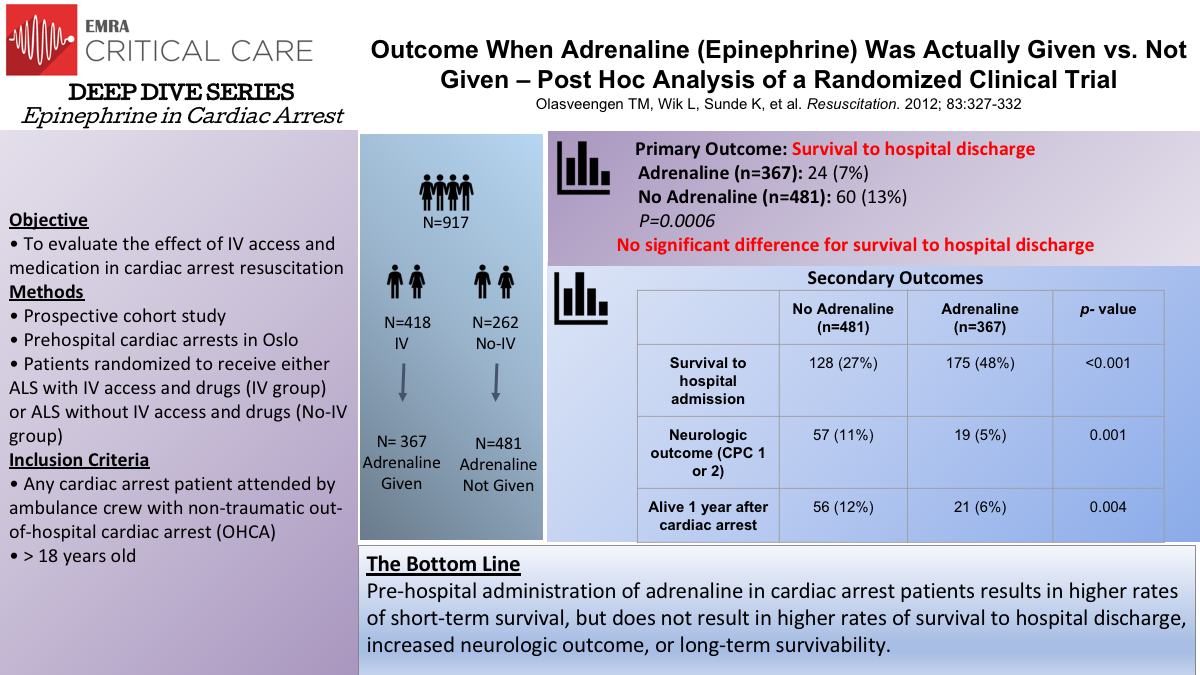
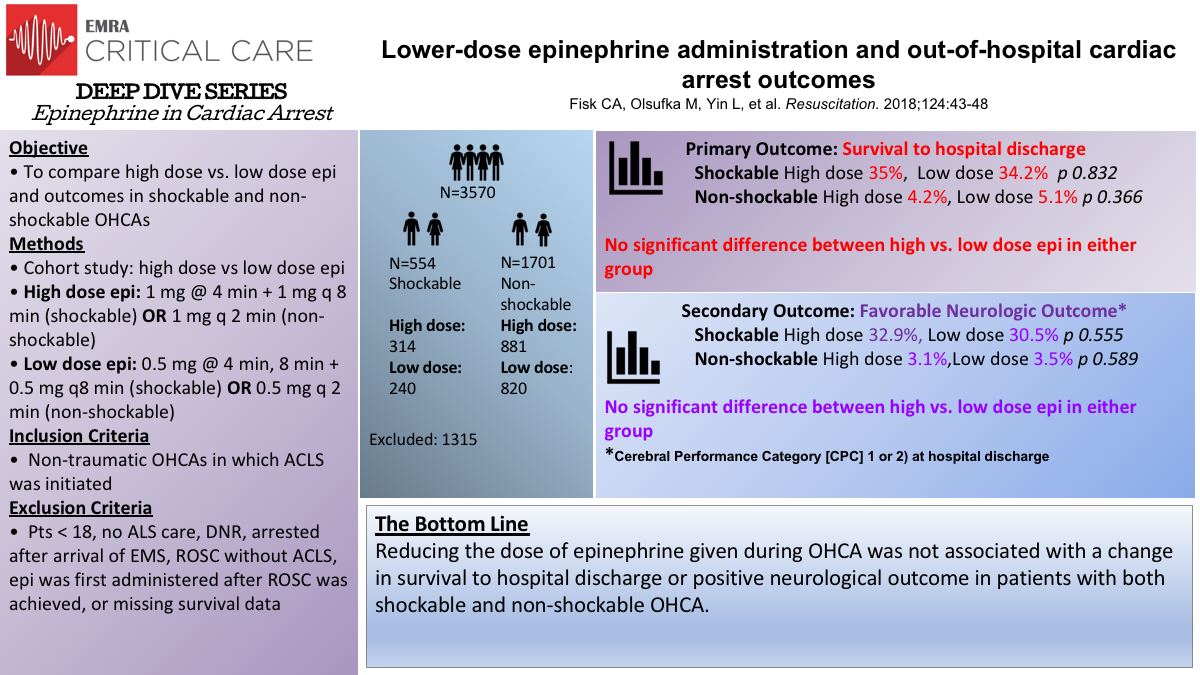
Epinephrine Dosage Cardiac Arrest - Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest. Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv). When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%.
Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv). When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%. Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest.
Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest. When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%. Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv).
Abstract 166 High Dose of Epinephrine Administered During
Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest. Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv). When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%.
Deep Dive into the Evidence Epinephrine in Cardiac Arrest EMRA
Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv). When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%. Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest.
Medication Review All About Epinephrine — EMS.Aware
When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%. Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest. Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv).
Deep Dive into the Evidence Epinephrine in Cardiac Arrest EMRA
When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%. Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv). Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest.
JCM Free FullText How Epinephrine Administration Interval Impacts
Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv). Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest. When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%.
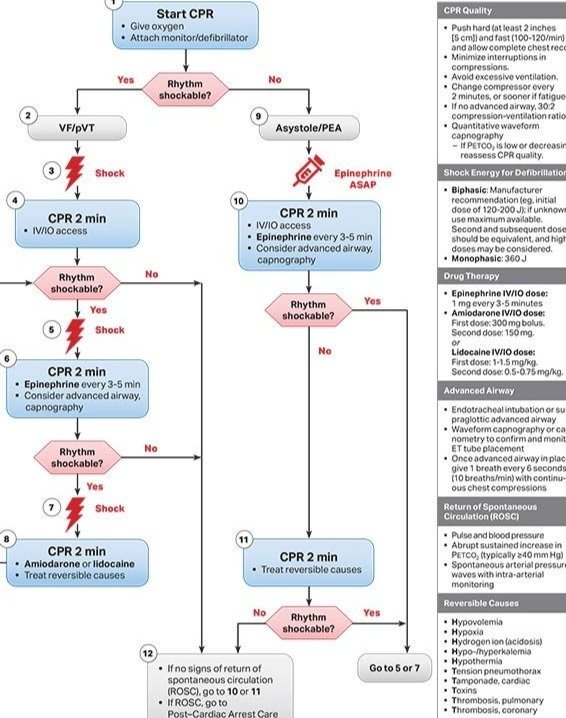
Part 7.2 Management of Cardiac Arrest Circulation
Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv). Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest. When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%.
Epinephrine in pediatric cardiorespiratory arrest when and how much
When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%. Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest. Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv).
Evaluation of Timing and Route of Epinephrine in a Neonatal Model of
When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%. Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest. Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv).
HighDose Epinephrine in Adult Cardiac Arrest NEJM
When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%. Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest. Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv).
Deep Dive into the Evidence Epinephrine in Cardiac Arrest EMRA
Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv). Current guidelines for both ohca and ihca recommend that epinephrine be given as soon as feasible when the initial cardiac arrest. When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%.
Current Guidelines For Both Ohca And Ihca Recommend That Epinephrine Be Given As Soon As Feasible When The Initial Cardiac Arrest.
When feasible, titrate fio2 to minimum necessary to achieve spo2 ≥94%. Standard dosing of epinephrine in resuscitation of adults experiencing cardiac arrest is 1 milligram (mg) administered either via intravenous (iv).