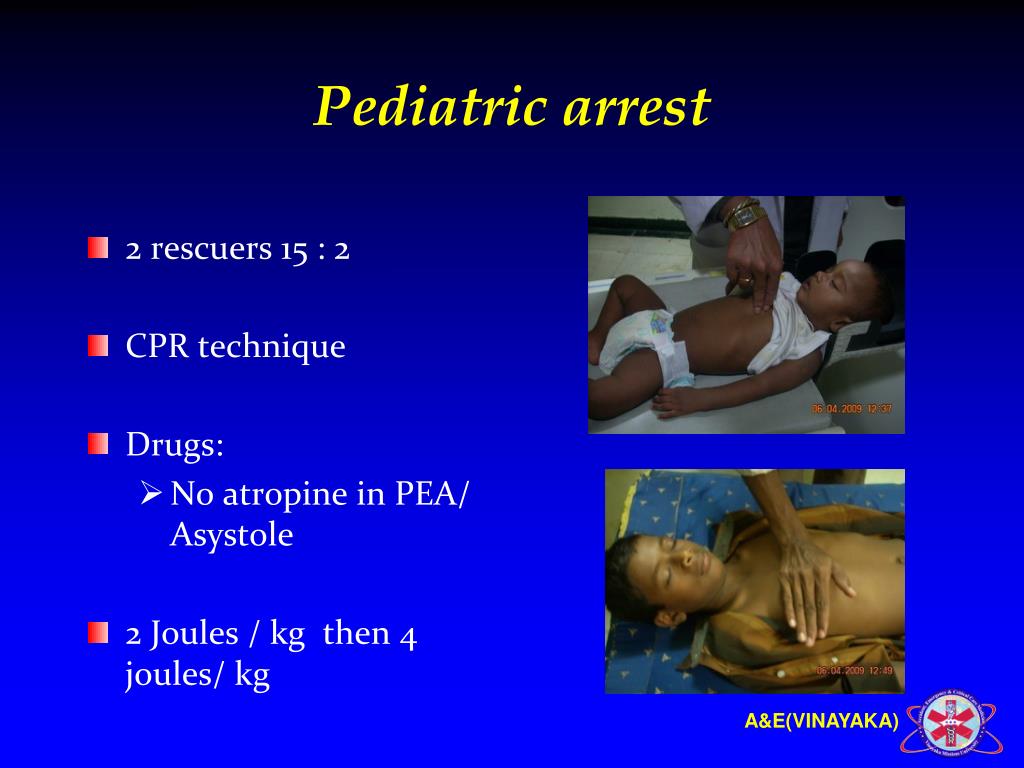
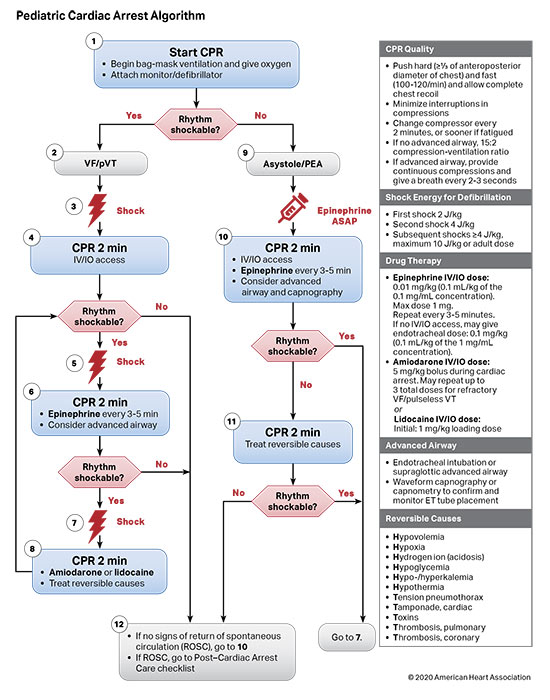
Infant In Cardiac Arrest - Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere.
Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the. Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere.
Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the.
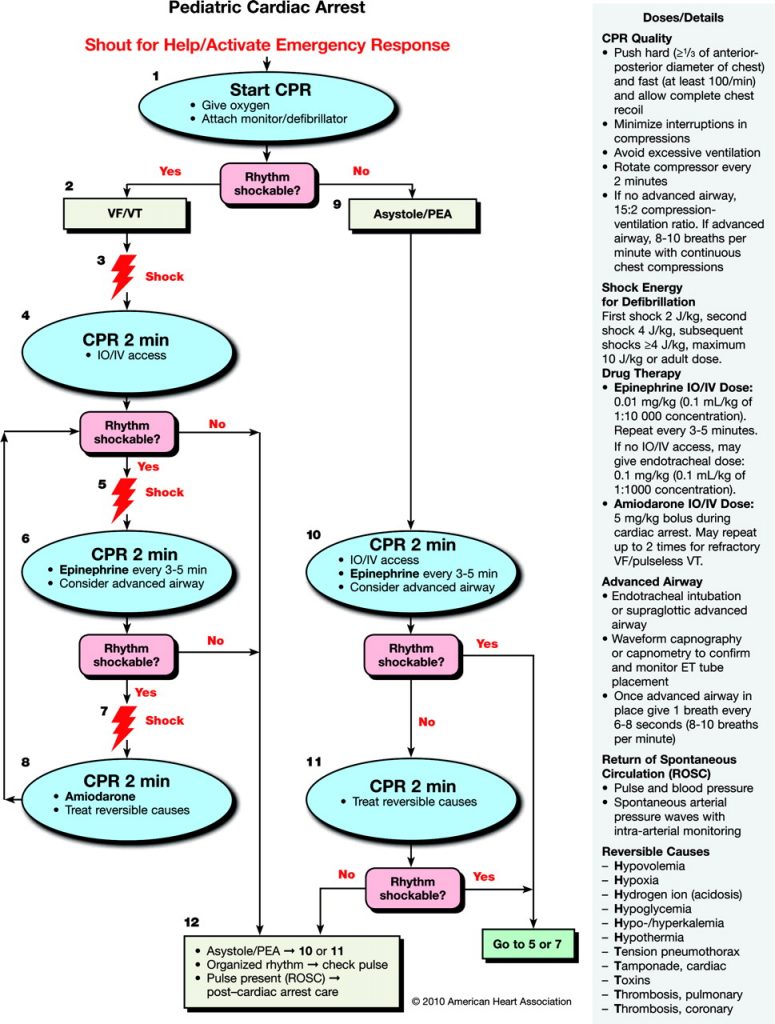
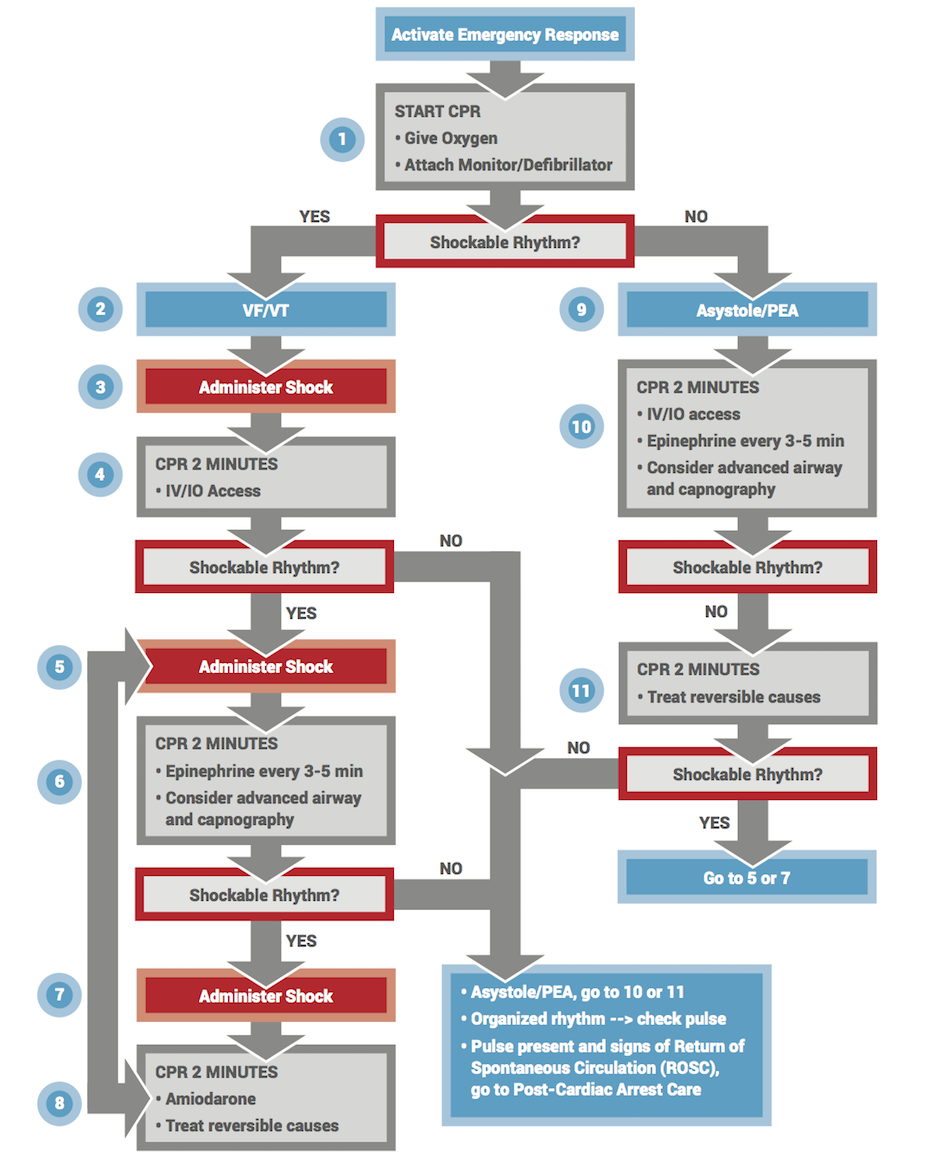
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Algorithm First10EM
Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere.
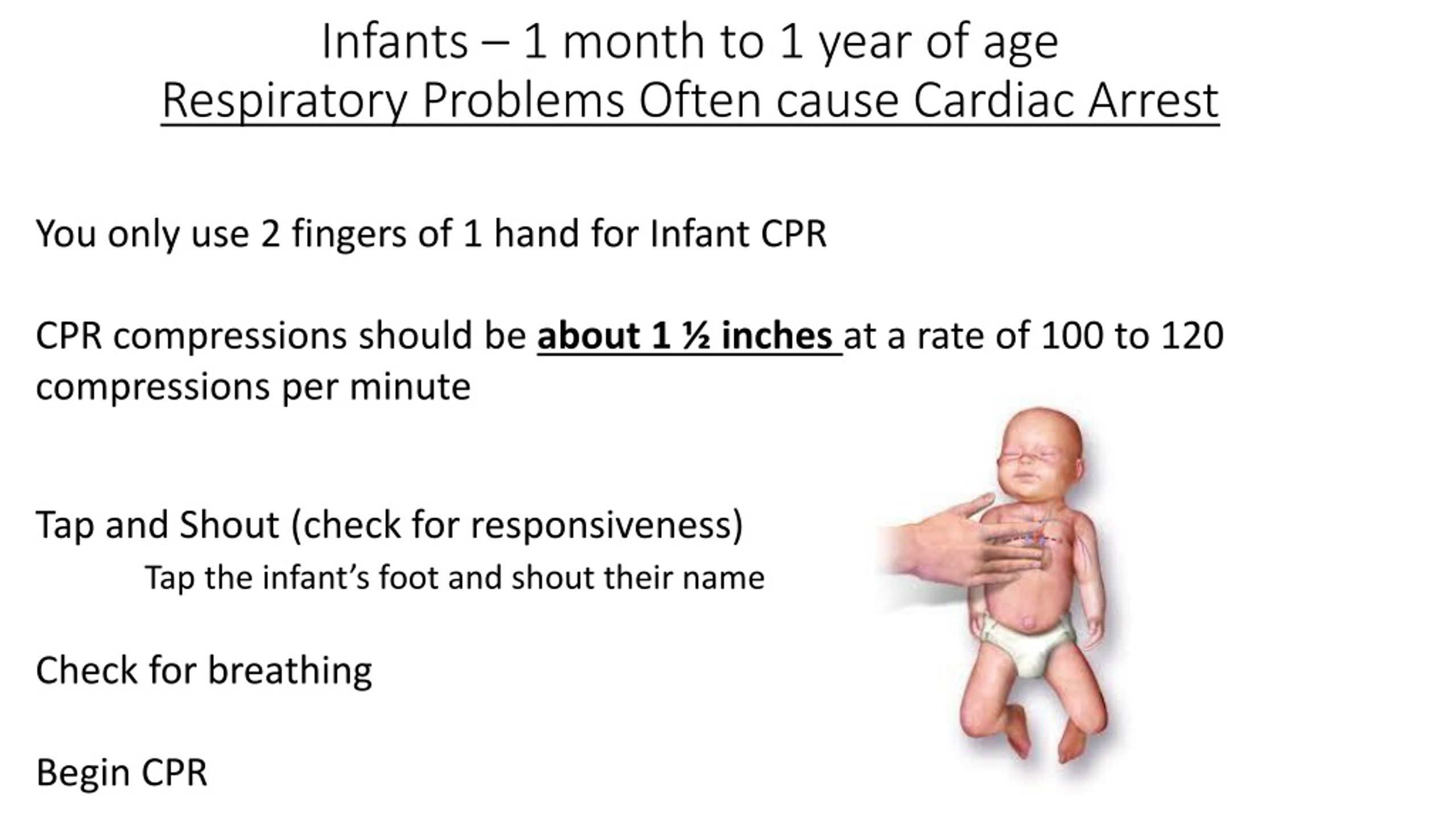
PPT CPR and AED Use for Infants PowerPoint Presentation, free
Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere.
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Infographic & Video
Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the. Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood.
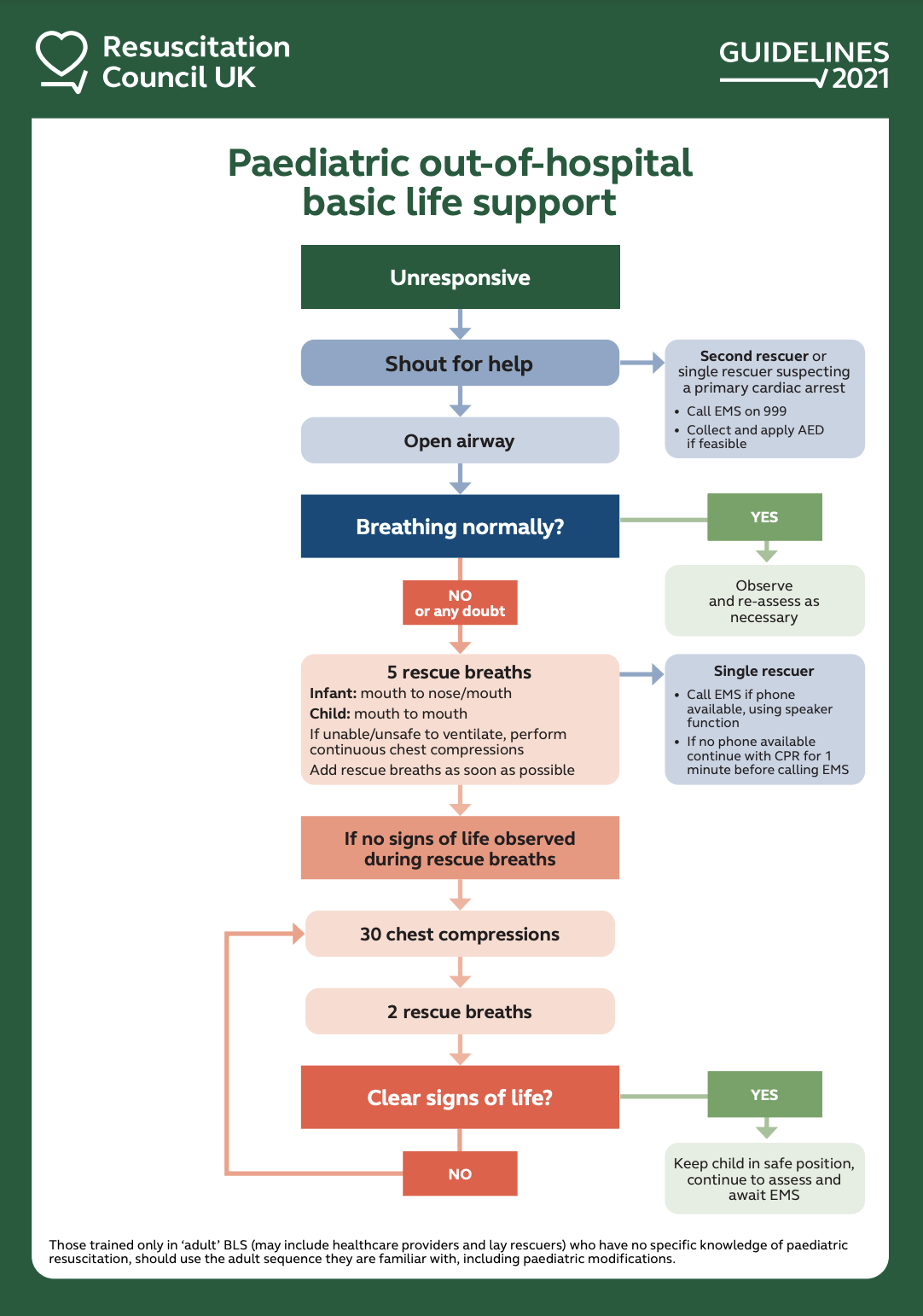
Paediatric basic life support Guidelines Resuscitation Council UK
Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the.
A SAFE baby The SAFE points in the SAFER protocol. © 20122020
Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the.
PPT CARDIAC ARREST PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1410743
Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere. Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the.
AHA 2015 pediatric cardiac arrest algorithm First10EM
Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere. Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood.
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest My EMS ConEd
Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the.
OCFD reviews pediatric cardiac arrest training, recertifies EMTs and
Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere. Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood.
Part 4 Pediatric Basic and Advanced Life Support American Heart
Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere. Mean diastolic blood pressure ≥25 mm hg during cpr in infants and ≥30 mm hg in children ≥1 year old was associated with 70% greater likelihood. Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the.
Mean Diastolic Blood Pressure ≥25 Mm Hg During Cpr In Infants And ≥30 Mm Hg In Children ≥1 Year Old Was Associated With 70% Greater Likelihood.
Recognizing cardiac arrest and activating the ems system, immediately beginning cpr, and using an aed as soon as possible gives the infant the. Cardiac arrest can happen anytime anywhere.