Item 12 Recent Research Indicates That Through Neuroplasticity - Neuroplasticity, the capacity of brain cells to change in response to intrinsic and extrinsic factors, can have negative or positive influence. We outline criteria for evaluating putative neuroimaging measures of plasticity in humans including links to neurobiological. Building on foundational developmental research, recent studies have uncovered novel insights into the mechanisms. Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining brain function, including learning and memory, as well as in. In this review, we explore the vast potential of neuroplasticity in various aspects of brain function across the lifespan and in the context. Recent neuroscientific research has identified specific activities that consistently promote neuroplastic changes.
We outline criteria for evaluating putative neuroimaging measures of plasticity in humans including links to neurobiological. Building on foundational developmental research, recent studies have uncovered novel insights into the mechanisms. Neuroplasticity, the capacity of brain cells to change in response to intrinsic and extrinsic factors, can have negative or positive influence. Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining brain function, including learning and memory, as well as in. Recent neuroscientific research has identified specific activities that consistently promote neuroplastic changes. In this review, we explore the vast potential of neuroplasticity in various aspects of brain function across the lifespan and in the context.
We outline criteria for evaluating putative neuroimaging measures of plasticity in humans including links to neurobiological. Building on foundational developmental research, recent studies have uncovered novel insights into the mechanisms. Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining brain function, including learning and memory, as well as in. In this review, we explore the vast potential of neuroplasticity in various aspects of brain function across the lifespan and in the context. Neuroplasticity, the capacity of brain cells to change in response to intrinsic and extrinsic factors, can have negative or positive influence. Recent neuroscientific research has identified specific activities that consistently promote neuroplastic changes.
Neuroplasticity The Brain’s SuperPower!
We outline criteria for evaluating putative neuroimaging measures of plasticity in humans including links to neurobiological. Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining brain function, including learning and memory, as well as in. Recent neuroscientific research has identified specific activities that consistently promote neuroplastic changes. In this review, we explore the vast potential of neuroplasticity in various aspects.
Neuroplasticity How Experience Changes the Brain
Building on foundational developmental research, recent studies have uncovered novel insights into the mechanisms. Neuroplasticity, the capacity of brain cells to change in response to intrinsic and extrinsic factors, can have negative or positive influence. Recent neuroscientific research has identified specific activities that consistently promote neuroplastic changes. We outline criteria for evaluating putative neuroimaging measures of plasticity in humans including.
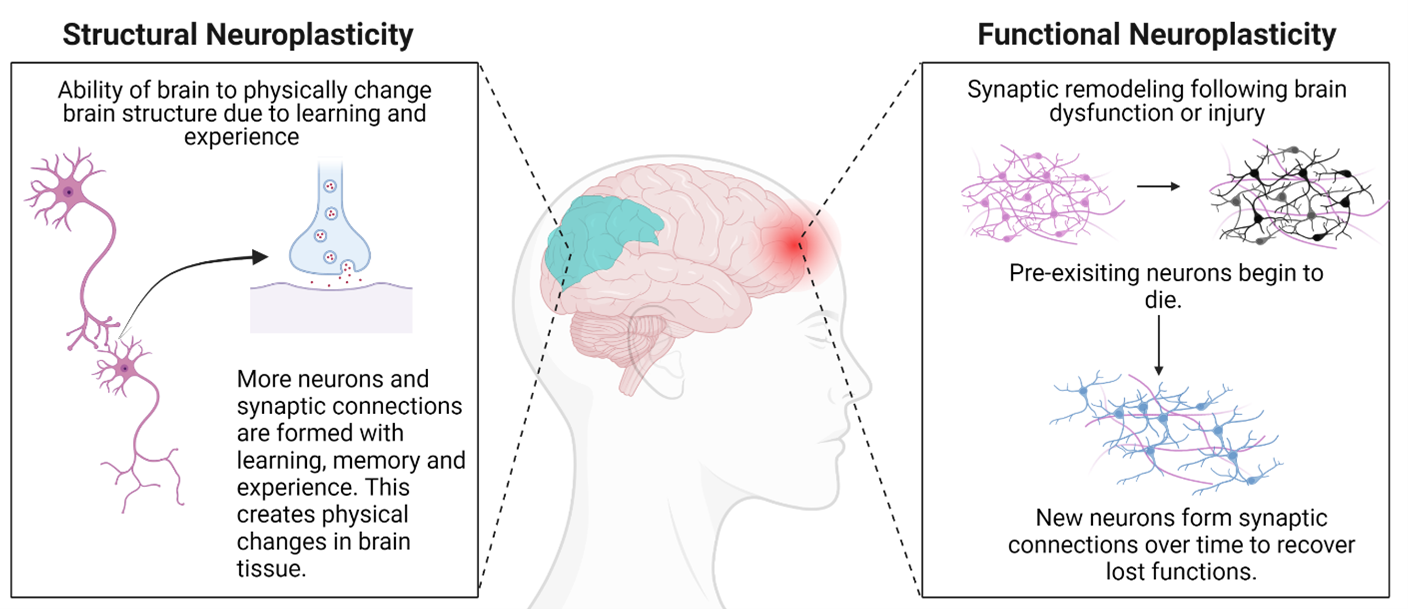
Schematic representation of neuroplasticity at different levels. (A
Neuroplasticity, the capacity of brain cells to change in response to intrinsic and extrinsic factors, can have negative or positive influence. Recent neuroscientific research has identified specific activities that consistently promote neuroplastic changes. Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining brain function, including learning and memory, as well as in. Building on foundational developmental research, recent studies have.
Neuroplasticity UC Davis Biotechnology Program
In this review, we explore the vast potential of neuroplasticity in various aspects of brain function across the lifespan and in the context. Neuroplasticity, the capacity of brain cells to change in response to intrinsic and extrinsic factors, can have negative or positive influence. Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining brain function, including learning and memory, as.
Neuroplasticity Is Most Evident in Which of the Following Circumstances
We outline criteria for evaluating putative neuroimaging measures of plasticity in humans including links to neurobiological. In this review, we explore the vast potential of neuroplasticity in various aspects of brain function across the lifespan and in the context. Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining brain function, including learning and memory, as well as in. Neuroplasticity, the.
Changes in cellular structures related to neuroplasticity. (2a
In this review, we explore the vast potential of neuroplasticity in various aspects of brain function across the lifespan and in the context. Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining brain function, including learning and memory, as well as in. Neuroplasticity, the capacity of brain cells to change in response to intrinsic and extrinsic factors, can have negative.
Plasticity of the aging brain New directions in cognitive neuroscience
Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining brain function, including learning and memory, as well as in. Neuroplasticity, the capacity of brain cells to change in response to intrinsic and extrinsic factors, can have negative or positive influence. Recent neuroscientific research has identified specific activities that consistently promote neuroplastic changes. We outline criteria for evaluating putative neuroimaging measures.
(PDF) and neuroplasticity in neurodevelopmental disorders
Building on foundational developmental research, recent studies have uncovered novel insights into the mechanisms. Recent neuroscientific research has identified specific activities that consistently promote neuroplastic changes. In this review, we explore the vast potential of neuroplasticity in various aspects of brain function across the lifespan and in the context. Neuroplasticity plays a crucial role in developing and maintaining brain function,.
The effects of positive and negative neuroplasticity on cognitive
Recent neuroscientific research has identified specific activities that consistently promote neuroplastic changes. We outline criteria for evaluating putative neuroimaging measures of plasticity in humans including links to neurobiological. Neuroplasticity, the capacity of brain cells to change in response to intrinsic and extrinsic factors, can have negative or positive influence. In this review, we explore the vast potential of neuroplasticity in.
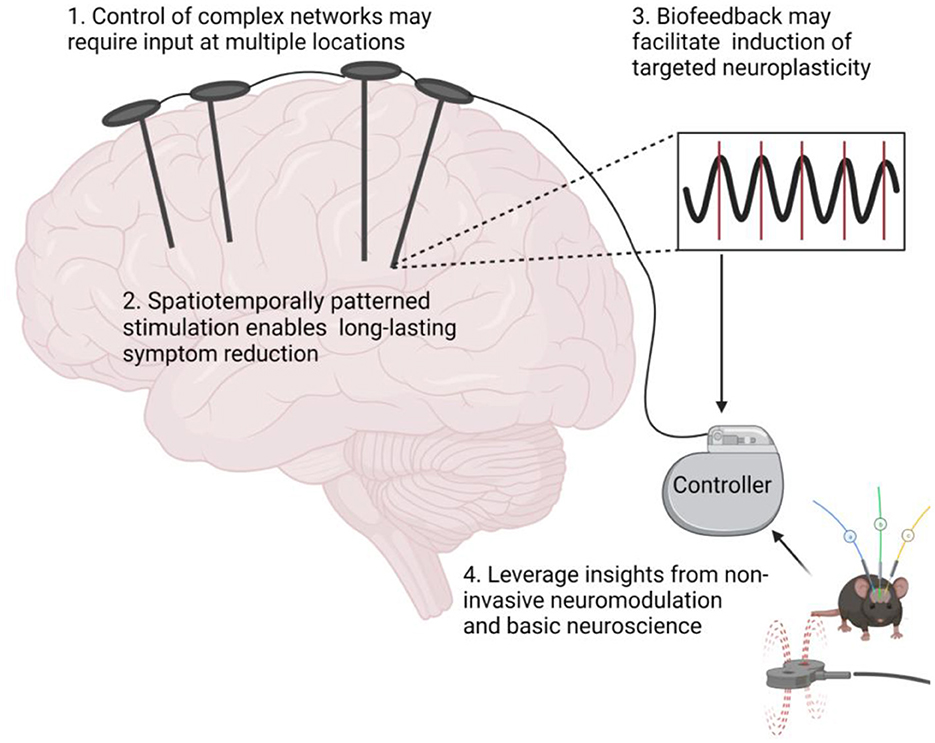
Frontiers Targeted neuroplasticity in spatiotemporally patterned
Recent neuroscientific research has identified specific activities that consistently promote neuroplastic changes. Neuroplasticity, the capacity of brain cells to change in response to intrinsic and extrinsic factors, can have negative or positive influence. Building on foundational developmental research, recent studies have uncovered novel insights into the mechanisms. In this review, we explore the vast potential of neuroplasticity in various aspects.
Recent Neuroscientific Research Has Identified Specific Activities That Consistently Promote Neuroplastic Changes.
Neuroplasticity, the capacity of brain cells to change in response to intrinsic and extrinsic factors, can have negative or positive influence. In this review, we explore the vast potential of neuroplasticity in various aspects of brain function across the lifespan and in the context. We outline criteria for evaluating putative neuroimaging measures of plasticity in humans including links to neurobiological. Building on foundational developmental research, recent studies have uncovered novel insights into the mechanisms.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-brain-plasticity-2794886-01-cb68ba43ed534fb4b220ff86bf28a0e4.png)