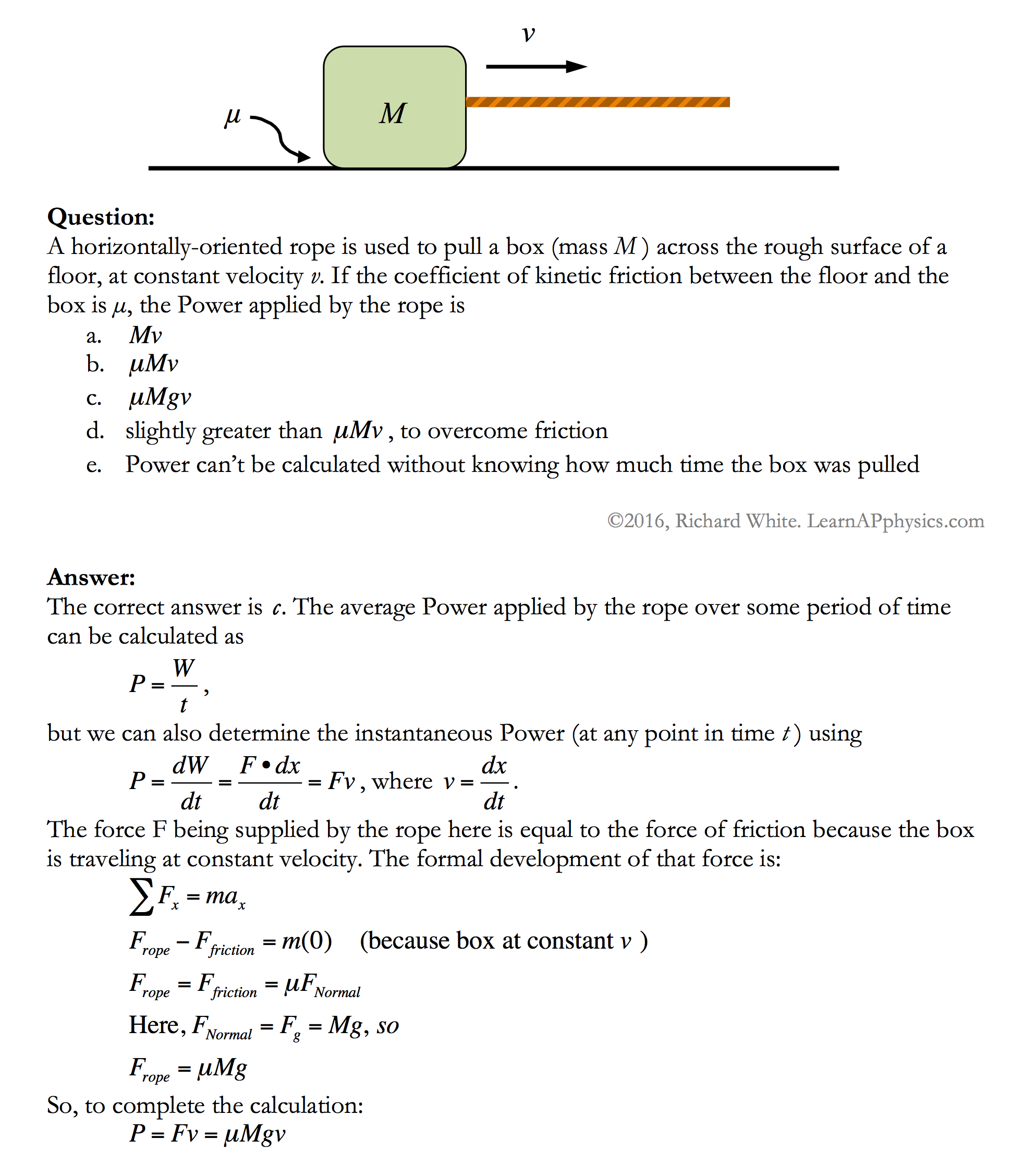
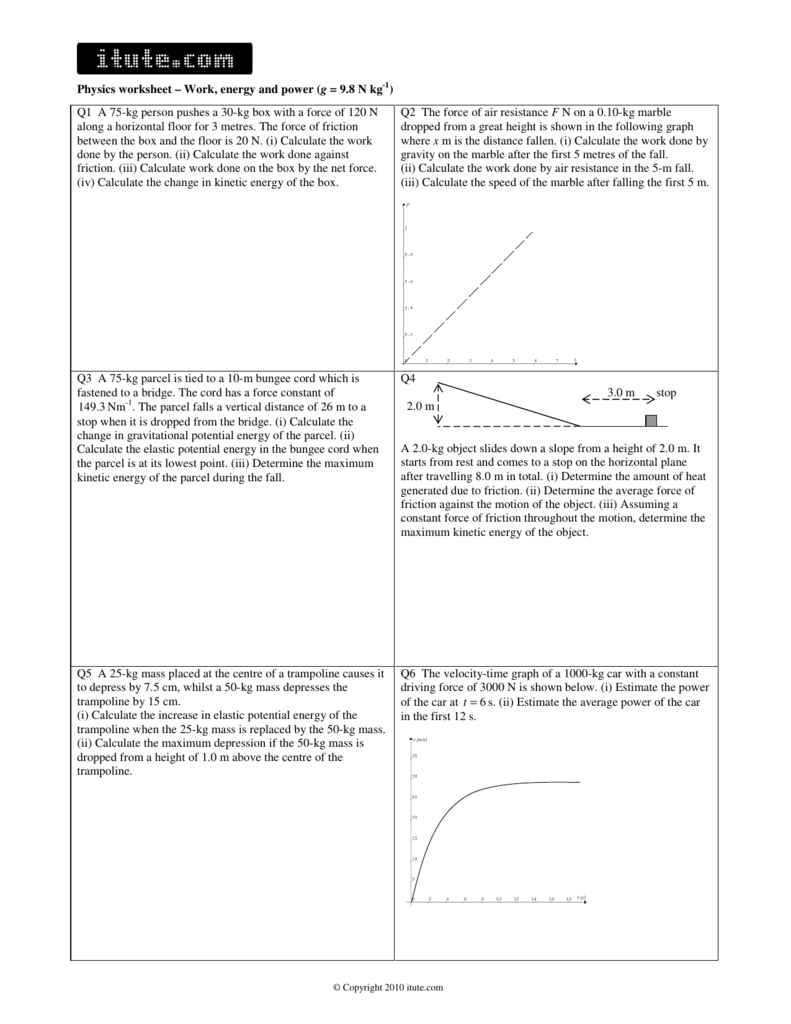
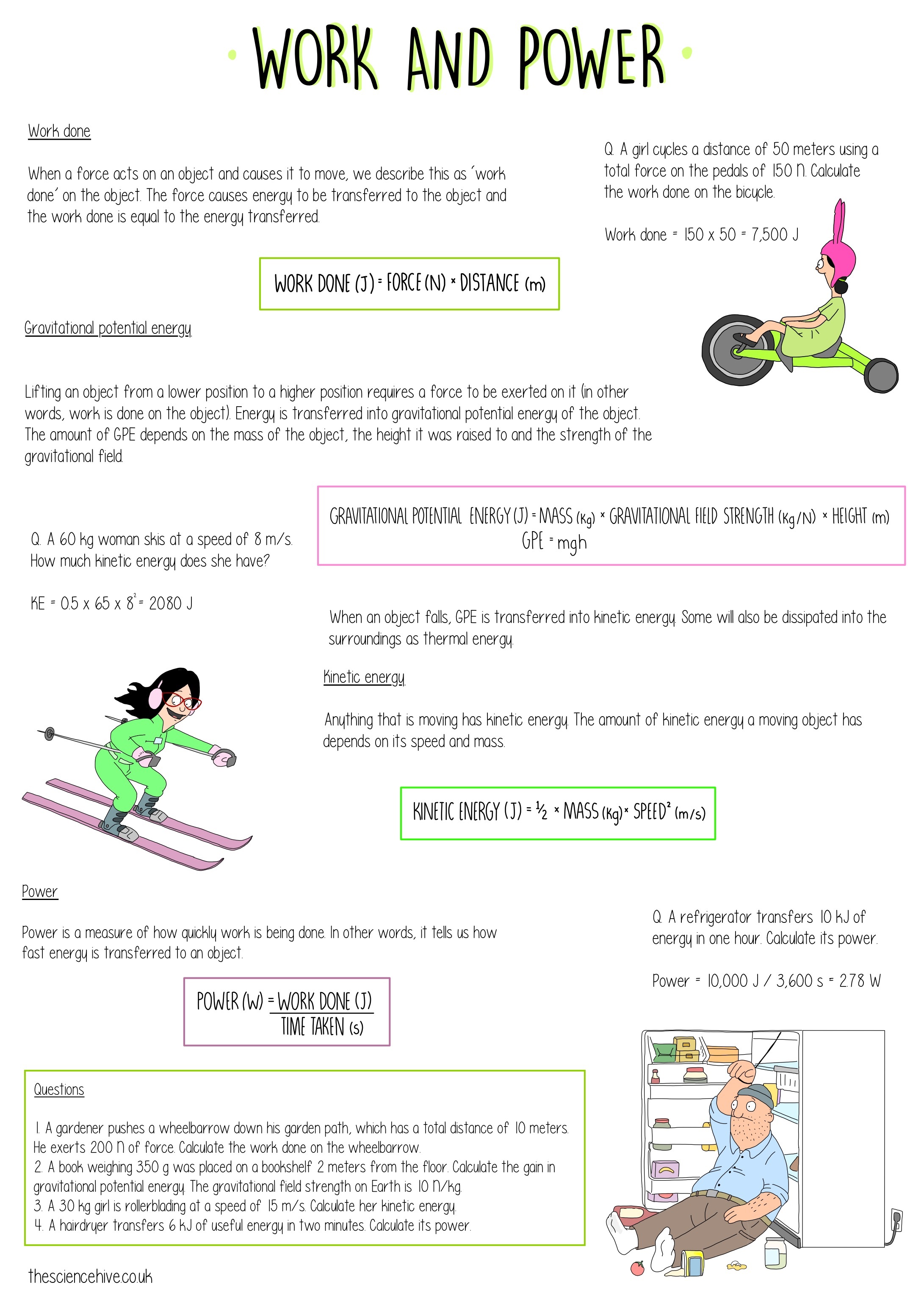
Work Power Energy Worksheet - You must exert a force of. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. Kinetic energy and potential energy 1. When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____. Calculate the kinetic energy of a 45 g golf ball travelling at: (a) 20 m/s, (b) 40 m/s, (c) 60 m/s. What is the difference between work and power? When the speed of an object doubles, does its. _____ is the rate at which work is done. These work power and energy worksheets will give students a chance to practice a variety of problems and activities to help students dive.
When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____. What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy? Kinetic energy and potential energy 1. _____ is the rate at which work is done. When the speed of an object doubles, does its. (a) 20 m/s, (b) 40 m/s, (c) 60 m/s. You must exert a force of. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. These work power and energy worksheets will give students a chance to practice a variety of problems and activities to help students dive. What is the difference between work and power?
These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. What is the difference between work and power? (a) 20 m/s, (b) 40 m/s, (c) 60 m/s. _____ is the rate at which work is done. What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy? These work power and energy worksheets will give students a chance to practice a variety of problems and activities to help students dive. Calculate the kinetic energy of a 45 g golf ball travelling at: When the speed of an object doubles, does its. When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____. You must exert a force of.
Worksheet Work Energy And Power
(a) 20 m/s, (b) 40 m/s, (c) 60 m/s. When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. When the speed of an object doubles, does its. These work power and energy worksheets will give students a chance to practice a variety of problems.
42 physics work and energy worksheet answers Worksheet Resource
When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____. You must exert a force of. _____ is the rate at which work is done. Kinetic energy and potential energy 1. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to.
Physics 11 Work Power Energy Worksheet Printable Worksheets And
_____ is the rate at which work is done. Kinetic energy and potential energy 1. When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____. These work power and energy worksheets will give students a chance to practice a variety of problems and activities to help students dive. (a) 20 m/s, (b) 40 m/s, (c) 60.
Work, Power and Energy Worksheet
Kinetic energy and potential energy 1. These work power and energy worksheets will give students a chance to practice a variety of problems and activities to help students dive. Calculate the kinetic energy of a 45 g golf ball travelling at: These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. What is the difference between work and power?
Worksheet Work Energy And Power
_____ is the rate at which work is done. (a) 20 m/s, (b) 40 m/s, (c) 60 m/s. When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____. Calculate the kinetic energy of a 45 g golf ball travelling at: Kinetic energy and potential energy 1.
Work Power And Energy Worksheets
_____ is the rate at which work is done. Calculate the kinetic energy of a 45 g golf ball travelling at: These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. When the speed of an object doubles, does its. What is the difference between work and power?
Free Collection of Work, Power, and Energy Worksheets
_____ is the rate at which work is done. You must exert a force of. Kinetic energy and potential energy 1. Calculate the kinetic energy of a 45 g golf ball travelling at: These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to.
Work And Power Worksheet
(a) 20 m/s, (b) 40 m/s, (c) 60 m/s. These work power and energy worksheets will give students a chance to practice a variety of problems and activities to help students dive. What is the difference between work and power? What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy? Kinetic energy and potential energy 1.
Physics Chapter 5 Work Power Energy Worksheet
Kinetic energy and potential energy 1. What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy? Calculate the kinetic energy of a 45 g golf ball travelling at: What is the difference between work and power? You must exert a force of.
Work Power And Energy Worksheets Answer Key
Calculate the kinetic energy of a 45 g golf ball travelling at: When calculating power, you should use the formula p = _____ divided by _____. These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. When the speed of an object doubles, does its. What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy?
_____ Is The Rate At Which Work Is Done.
These problem sets focus on the use of energy principles to. Kinetic energy and potential energy 1. What is the difference between work and power? These work power and energy worksheets will give students a chance to practice a variety of problems and activities to help students dive.
Calculate The Kinetic Energy Of A 45 G Golf Ball Travelling At:
What is the difference between kinetic and potential energy? (a) 20 m/s, (b) 40 m/s, (c) 60 m/s. When the speed of an object doubles, does its. You must exert a force of.